In this rapidly evolving cryptocurrency landscape, crypto-malware has emerged as a significant threat as cryptocurrencies grow in popularity and value. Crypto-malware is malicious software that exploits a computer’s processing power to mine cryptocurrencies without the user’s permission. This type of malware became prominent as cryptocurrencies gained value, with the first known cryptojacking incidents marking its rise.
However, in this article, we’ll delve deeper into crypto-malware, how it happens, how to safeguard against it, and much more. So, read till the end for a complete understanding of crypto-malware.
What is Crypto Malware?
Crypto malware is a type of malicious software specifically designed to exploit the processing power of computers or devices to mine cryptocurrencies without the user’s permission. This process, known as cryptojacking, involves the malware secretly using the device’s resources to mine digital currencies like Monero, which are chosen for their strong privacy features that make them hard to track.
The unauthorized mining activity leads to increased CPU usage, slower device performance, overheating, and higher electricity bills. Crypto malware often spreads through infected email attachments, malicious links, compromised websites, and software vulnerabilities.
How Did Crypto Malware Emerge in the Crypto Landscape?
Crypto malware emerged in the cryptocurrency landscape as these digital assets gained popularity and value. The first known cryptojacking script was released by Coinhive in 2017, enabling website owners to embed mining code on their sites to use visitors’ computing power for mining. This marked the beginning of a surge in crypto malware attacks.
Cybercriminals quickly adopted these techniques, finding cryptojacking more attractive than other forms of cyberattacks like ransomware. Cryptojacking is less likely to attract law enforcement attention, is relatively low-risk, and highly profitable. As cryptocurrencies like Monero, which offer enhanced privacy, became popular, so did the use of crypto-malware to mine them.
Hackers utilize various methods to carry out crypto malware attacks, such as embedding malicious mining scripts in ads and websites, exploiting software and operating system vulnerabilities, and even targeting weaker security in Internet-of-Things (IoT) devices.
How to Safeguard Against Crypto Malware
To safeguard against crypto-malware, consider the following measures:
- Regular Software Updates: Regularly update your operating system and software to ensure you have the latest security patches that protect against known vulnerabilities.
- Use Trusted Antivirus Software: Use strong antivirus and anti-malware programs that can detect and remove crypto malware. Many of these programs offer real-time protection against threats.
- Be Cautious with Emails: Avoid opening email attachments or clicking on links from unknown or suspicious sources. Cybercriminals often use phishing emails to spread malware.
- Download Software from Authentic Websites: Only download software from reputable websites and developers to reduce the risk of encountering malware-laden programs.
- Use a Firewall: Enable a firewall on your computer to block unauthorized access and filter incoming and outgoing traffic, adding an extra layer of protection.
- Monitor CPU Usage: Regularly check your device’s CPU usage through tools like Task Manager (Windows) or Activity Monitor (macOS). Unexplained high CPU usage might indicate a crypto malware infection.
By following these practices, you can reduce the chance of falling victim to crypto malware attacks.
How to Identify Crypto Malware
Identifying crypto malware involves looking for several key signs that may indicate your device has been compromised. Here are some ways to spot it:
- Increased CPU Usage: Crypto malware typically hijacks your computer’s processing power. If you notice a sudden and sustained spike in CPU usage, especially when your computer is idle, this could be a sign of crypto-malware.
- Slow Performance: Because crypto malware uses a significant portion of your CPU resources, it often causes your device to run slowly. This sluggish performance can affect all aspects of your computer’s operation, from opening applications to browsing the web.
- Overheating and Noisy Fans: Increased CPU activity can cause your computer to overheat, making your fans work harder to cool it down. If you notice your device is hotter than usual or the fans are running loudly for no apparent reason, it might be due to crypto-malware.
- Unusual Network Activity: Crypto malware often communicates with external servers to receive instructions or send mined data. Monitoring your network traffic for unusual patterns or connections to unknown servers can help identify an infection.
Difference Between Crypto Malware and Ransomware
Crypto Malware: Crypto malware is designed to secretly mine cryptocurrencies using the victim’s computer resources without their consent. This malicious software runs quietly in the background, exploiting system and browser vulnerabilities, which makes it hard to detect.
The impact of crypto-malware includes slow performance, high CPU usage, overheating, and increased electricity bills due to the intensive computing tasks it performs. Hackers profit from crypto-malware by mining digital currencies, which they can later exchange for real money.
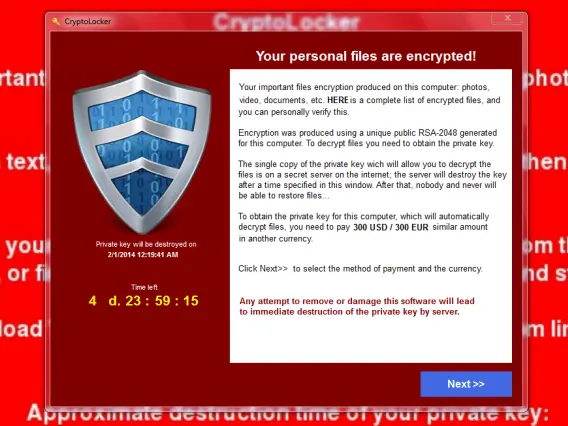
Ransomware: Ransomware, on the other hand, encrypts files on the victim’s computer and demands a ransom for their decryption. It typically spreads through phishing emails, malicious attachments, or by exploiting software vulnerabilities.
Once activated, ransomware locks files and displays a ransom note with payment instructions, making its presence immediately known. The impact of ransomware is significant, as it makes critical files inaccessible, potentially leading to data loss and operational downtime for businesses. Hackers profit by extorting victims for money, usually in the form of cryptocurrencies, in exchange for a decryption key to restore access to the encrypted files.
Conclusion
Crypto malware is malicious software that covertly uses a device’s processing power to mine cryptocurrencies, leading to increased CPU usage, slower performance, overheating, and higher electricity bills. Cybercriminals prefer it over other attacks like ransomware due to its lower risk and high profitability. By understanding what crypto-malware is and implementing effective safeguards, you can protect your devices and personal data from this growing threat. Stay vigilant and informed to navigate the evolving cryptocurrency landscape securely.
I am Pawan Kashyap currently living in Amritsar. I always try to grab new things from the cryptocurrency market. From my observations and trends in the market, I always try to provide the best and accurate information in the form of articles from this blog. Follow us on Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter to join us.